Simple fits tool¶
This tool is used to do simple fits on many data sets quickly. Ideally, one setups the Q range and fitting conditions on one or two data sets and runs the tool on all of the data selected in the listbox. Assuming q range and model are suitable for all, user gets quickly table or graph of results.
Implemented models:
Guinier
Porod
Sphere
Spheroid
Guinier Rod
Guinier Sheet
Invariant
1D Correlation
Power Law
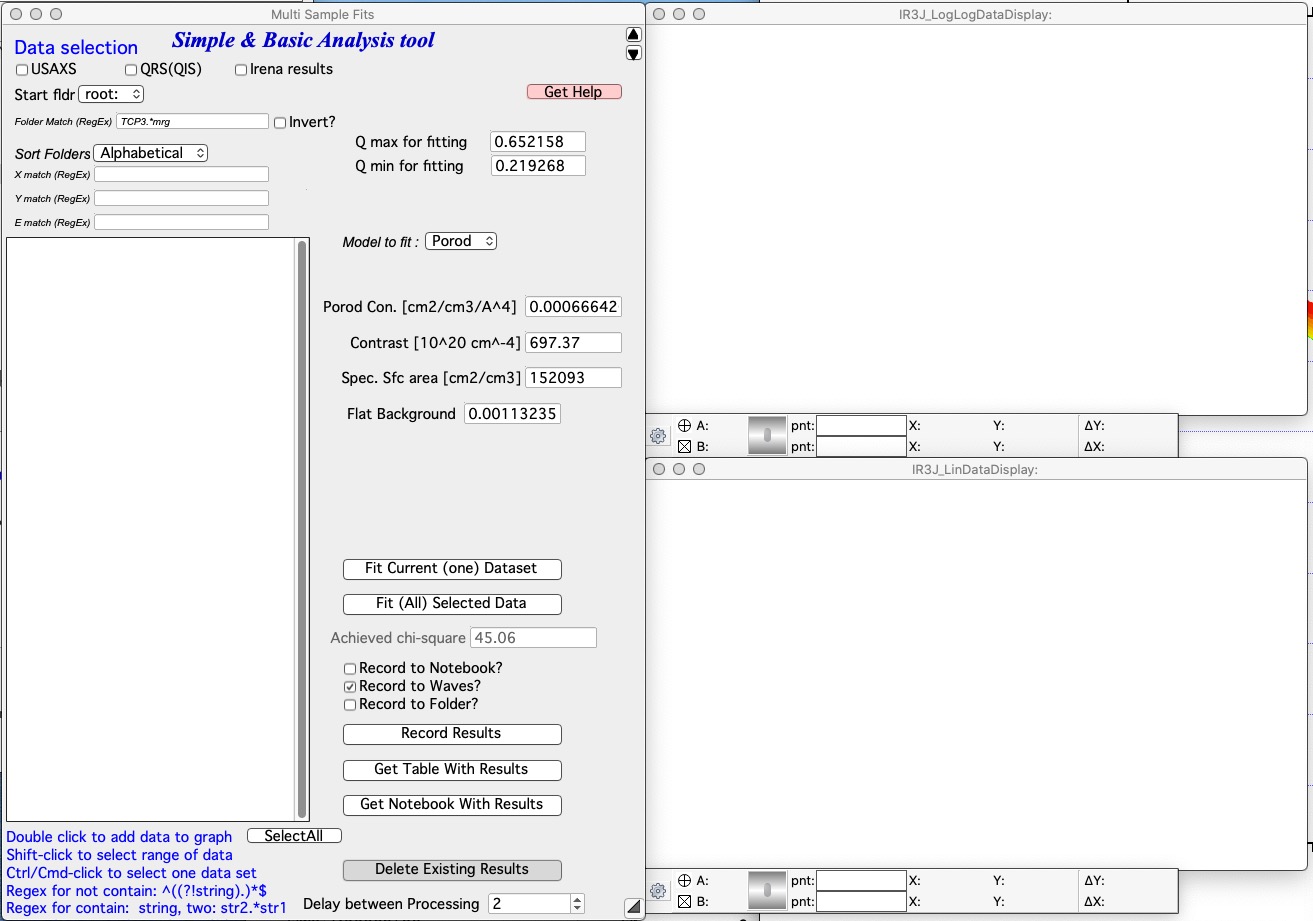
Selecting data
Understanding data selection tools makes user life easier. In the Data selection part of the panel you need to define sufficiently the data you want to look inside. There is detailed description on how to use this widget system Multi Data selection. Please refer to that page for details. This tool can use three types of data - USAXS, QRS (SAXS or WAXS) as well as Irena results (results saved by other Irena tools). All SAXS/WAXS data which DO NOT come from APS USAXS instrument use QRS naming system. Only if you have our USAXS data, you should use USAXS data type. For everyone else, use QRS naming system that is how your data came through ASCII importer or through Nika. For Irena results, there are two meaningful tools to be applied - Volume and Number Size distribution results.
You need to select Start fldr (e.g., “root:SAXS:”) and data type using Folder Match (e.g., “sub”).
Add data using double click Add data using double click. Data are always added to the top graph as log-Intensity vs log-Q. For some (Guinier, Porod,…) the lower graph presents linearization plot. For some (Sphere) no linearization plot is presented.
Select Q range to fit a specific model and push button Fit Current (One) Dataset. Results are presented, see image with really ugly Guinier fit or much better fit for spheroid…
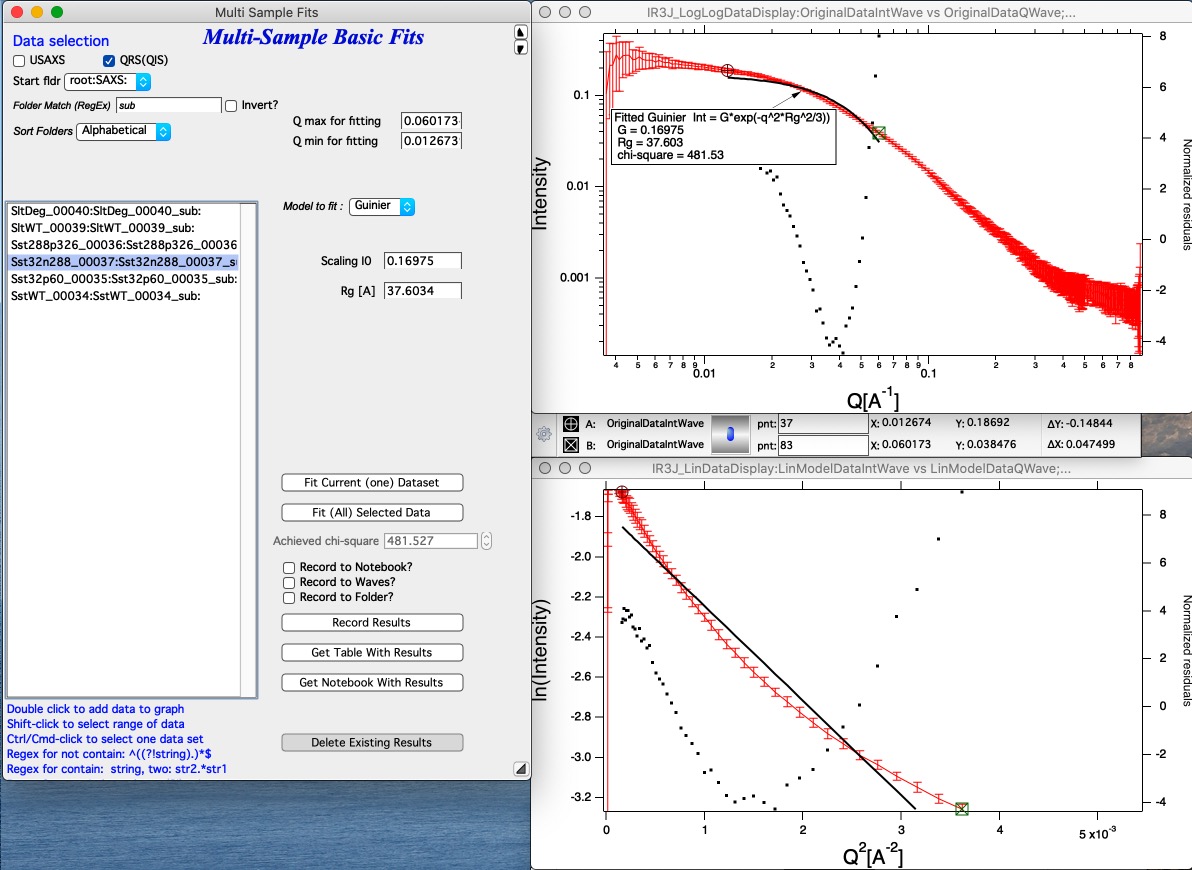
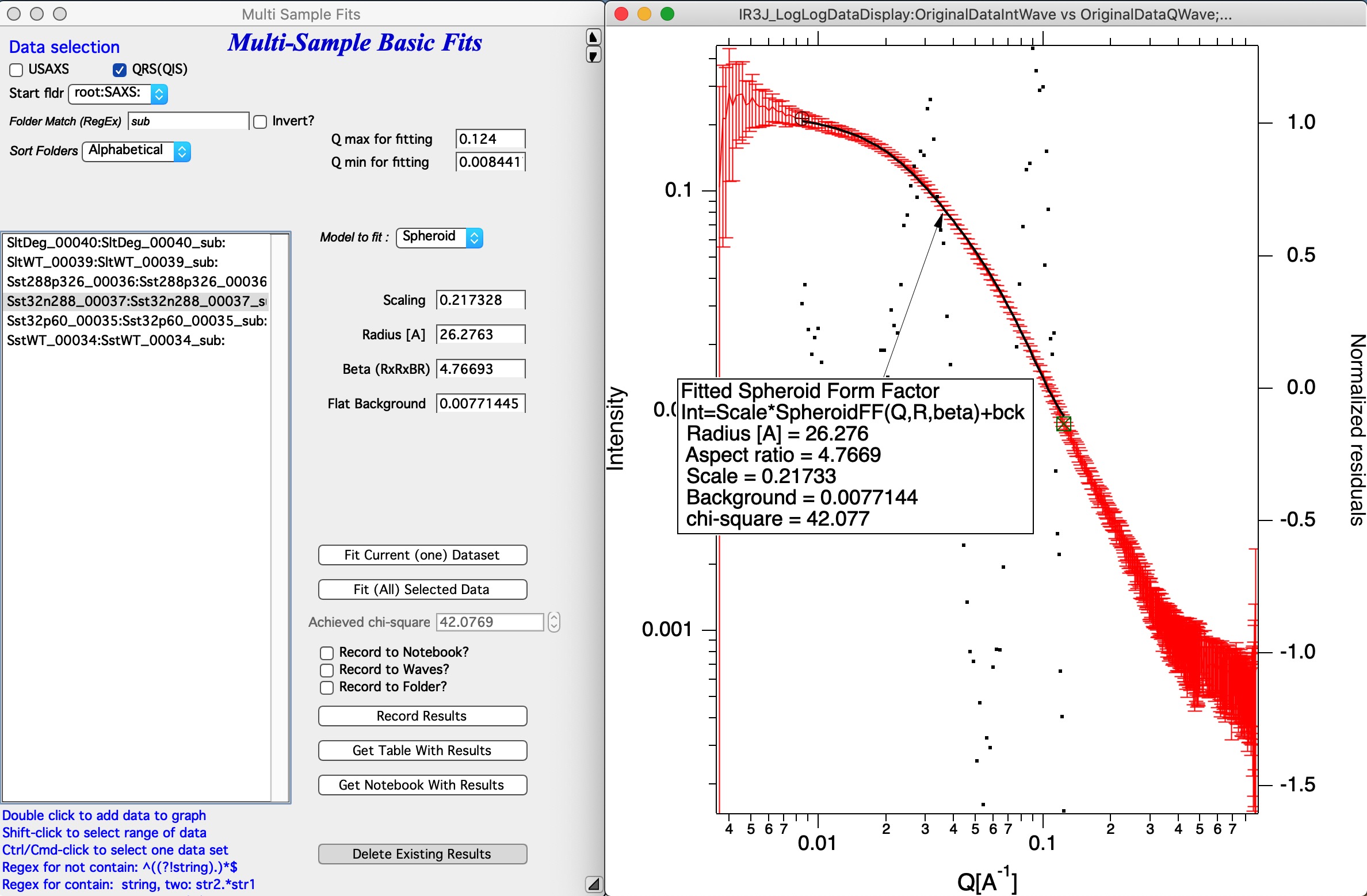
Note value for chi-square for goodness of fit.
Now, user can save the fitted results. Results can be saved in three ways suing the three checkboxes on the panel:
Results can be recorded in Notebook. This can be opened using Get Notebook With Results button.
Waves containing resulting values - and text wave with folder name - in Igor folder (root:NameDependingOnMethod). User can create table with those results using button Get Table With results. Also, user can manually graph any of those values as needed.
Results can be saved in the folder where the data came from. In this case waves with fitted Int-Q are created and results are placed in wave notes. User can plot these using Irena plotting tools (these are Irena results type) and look through the wave note values later using Metadata Browser.
Run as sequence
User can select multiple data sets in the listbox, method to use, Q range to use, and way to store results and run same analysis method on sequence of the data. Note, that data are processed in the order (from top to bottom) they are displayed in the Listbox. It is really useful to order the processing in meaningful order (time, temperature, etc.) which then results in the tables being in suitable order.
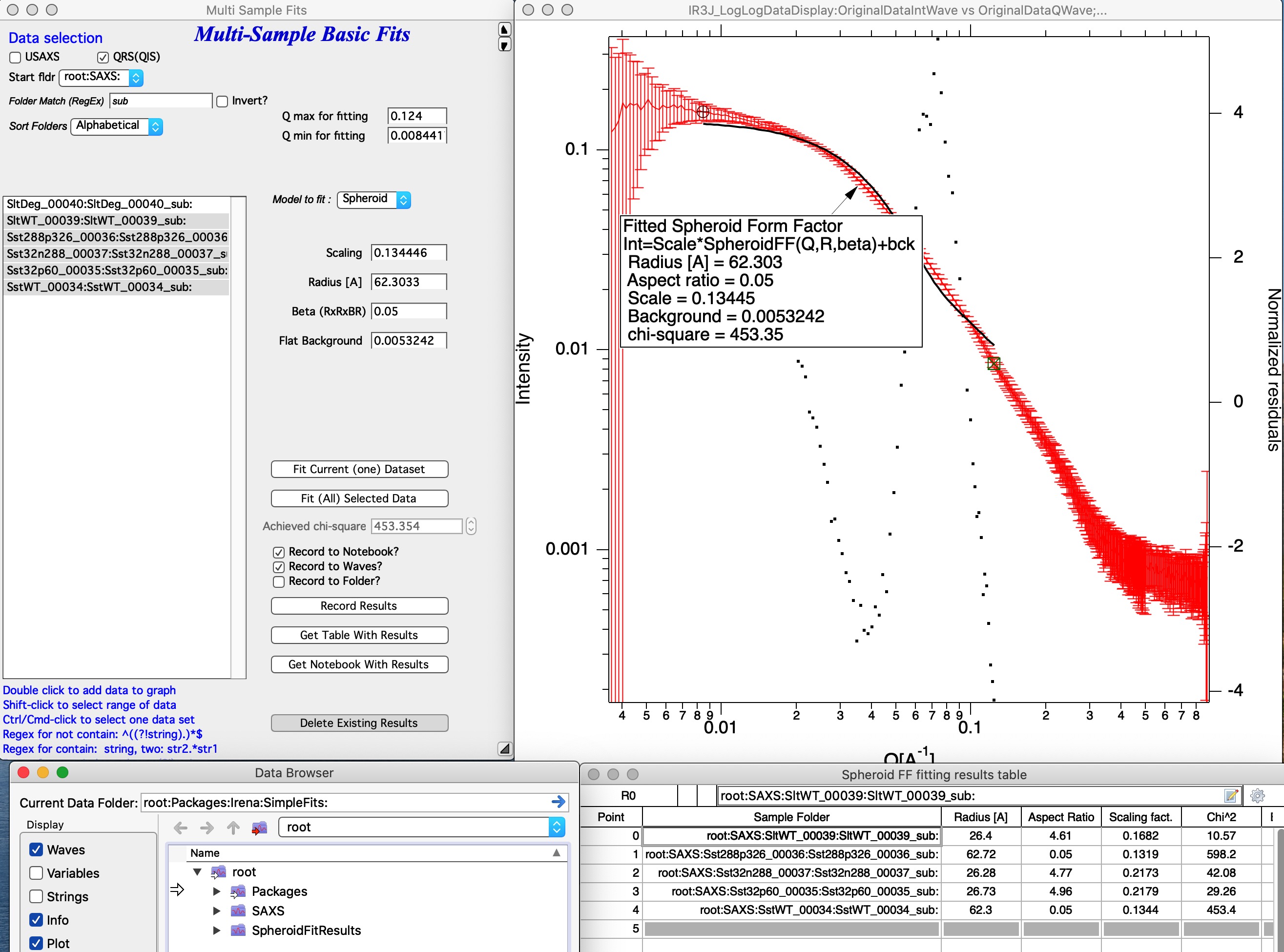
In the image one can see results of run of Spheroid model on sequence of data sets. Code run 5 data sets, created new folder in Igor experiment root:SpheroidFitResults and stored there many waves with results of the model. It then created a table with these values and displayed for user. User can now go and manually utilize the model results in their own graphs or subsequence processing. I also stored data in notebook, but that is not shown here - it contains summary of resulting values and graph for each sample which was run.
Delete Existing results This button will close table with results and delete the folder root:SpheroidFitResults (or similarly named folder with results from different fitting model). Be careful, there is no recovery for this.
Models supported:¶
Guinier
Fits Guinier law.
Porod
Fits Porod’s law.
Sphere
Fits simple form factor of sphere
Spheroid
Fits simple form factor of spheroid.
Guinier Rod
Fits Guinier if the shape is infinite rod.
Guinier Sheet
Fits Guinier if shape is infinite sheet.
Invariant
Calculates invariant with background subtraction.
Power Law
Fits Power law formula \(Int = Pref * Q^{-Exp} + Bckg\)
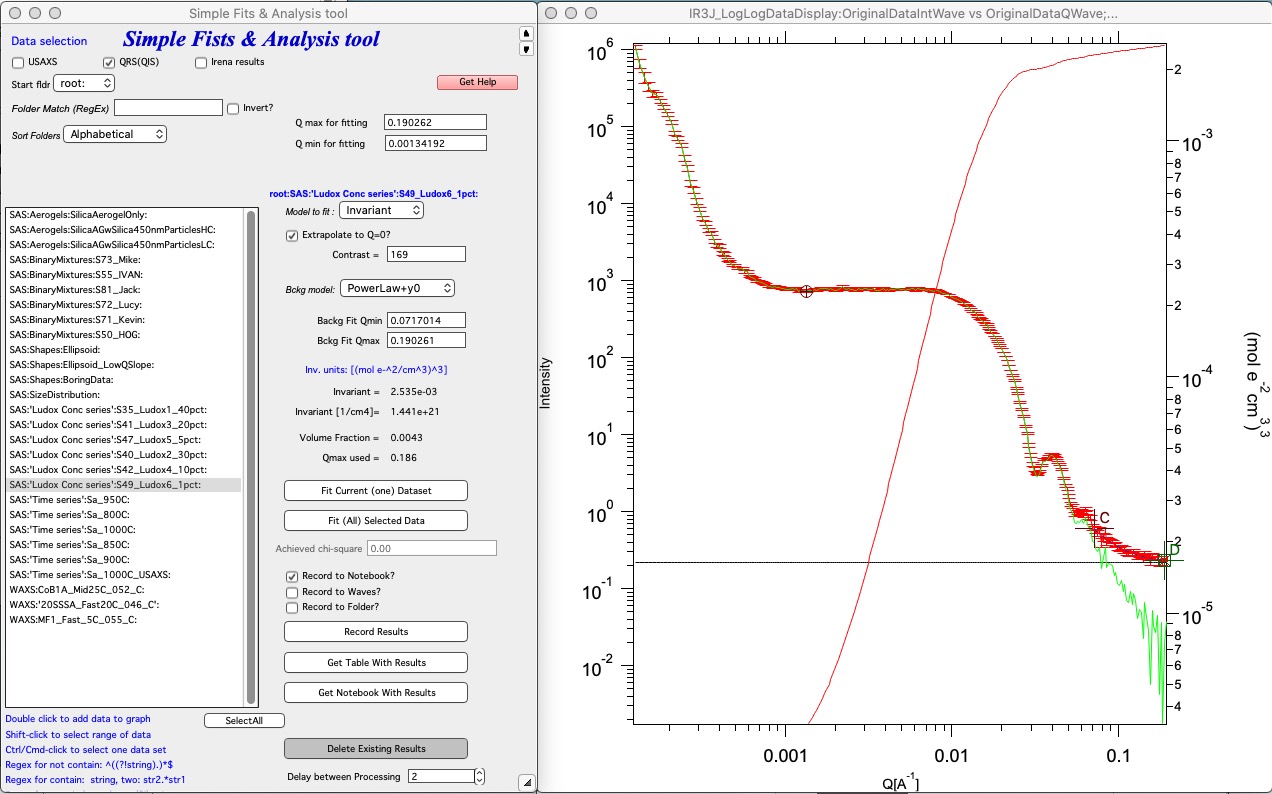
To use select the “Invariant”, double click on suitable data. That will add into graph. Then select range of data from which you want to calculate invariant with cursors A and B (round and rectangle). Ideally use “Extrapolate to Q=0”. Input contrast to have results on absolute scale (requires absolute calibration of intensity). Select background subtraction model and use cursors C and D (crosses) to select range, where background function is fitted. Black horizontal line represents calculated flat background. Results are below and can be saved using choices (Record to Notebook or Waves). There is nothing to record to Folder here as that requires output (model) waves.
1D Correlation
- This procedure calculates the 1D correlation function as typically seen used to analyze lamellar structures. There are 3 choices:
- * Calculate K(z) as typically reported by Strobl. The result is reported in units of (mol e-/cm^3)^2. I’m not confident in the data scaling in this case.* For an anisotropic (highly oriented) lamellar morphology, calculate Gamma(z) as derived by Vonk & Kortleve, but following Roe’s book.* For an isotropic lamellar morphology (very common), calculate gamma(z) as in #2 but applying a Lorentz-type correction to I(q) first.
Z input (maximum Z in real space) must be in same units as q (nm and 1/nm, or Ang and 1/Ang) Needs to know wavelength, input wavelength in A. Default is Cu wavelength.
- References:
- Litvinov et al, Macromolecules 2011, 44, 9254.Vonk, C. G.; Kortleve, G. Kolloid-Zeitschrift und Zeitschrift für Polymere 1967, 220(1), 19-24.Strobl, G. R. Journal of Applied Crystallography 1973, 6(5), 365-370.Strobl, G. R.; Schneider, M. Journal of Polymer Science Part B-Polymer Physics 1980, 18(6), 1343-1359.Roe, R.J. Methods of X-ray and Neutron Scattering in Polymer Science.
Clasical electron radius = re = 2.8179e-15 m = 2.8179e-13 cm